Register and Use the service by DI
DI (Dependency Injection) is one of the core mechanisms of OpenSumi framework. By using DI, we can easily achieve the decoupling of dependencies and reuse of services. For more details, please see Dependency Injection .
This section will start from use cases. Rgister ITodoService service When you are using the IMessageService service offered by the framework. Todo items switch state to display handover information.
Registration Service
Declare ITodoService service interface:
export interface ITodoService {
showMessage(message: string): void;
}
export const ITodoService = Symbol('ITodoService');Implement ITodoService services:
import { Injectable, Autowired } from '@opensumi/di';
import { IMessageService } from '@opensumi/ide-overlay';
import { ITodoService } from '../common';
@Injectable()
export class TodoService implements ITodoService {
showMessage(message: string) {
console.log(message);
}
}Register the ITodoService service and its corresponding implementation:
import { Provider, Injectable } from '@opensumi/di';
import { BrowserModule } from '@opensumi/ide-core-browser';
import { TodoService } from './todo.service';
import { ITodoService } from '../common';
@Injectable()
export class TodoListModule extends BrowserModule {
providers: Provider[] = [
{
token: ITodoService,
useClass: TodoService,
},
...
];
}
Use Custom Services
In the view, we make useInjectable hook function as a service to register DI in the view layer. We can elicit the ITodoService instance and use it by implementing the following code:
export const Todo = ({
viewState
}: React.PropsWithChildren<{ viewState: ViewState }>) => {
const { showMessage } = useInjectable<ITodoService>(ITodoService);
};Use Built-in Services
Message Notification
All the capabilities in OpenSumi basically exist in the form of DIs, which can be easily introduced and used. For example, if we need a message notification feature, we can use IMessageService to get and use that feature.
import { Injectable, Autowired } from '@opensumi/di';
import { IMessageService } from '@opensumi/ide-overlay';
import { ITodoService } from '../common';
@Injectable()
export class TodoService implements ITodoService {
@Autowired(IMessageService)
private messageService: IMessageService;
showMessage = (message: string) => {
this.messageService.info(message);
};
}By binding the trigger function when the Todo item is clicked, you can use the IMessageService to display the message directly.
export const Todo = ({
viewState
}: React.PropsWithChildren<{ viewState: ViewState }>) => {
const { width, height } = viewState;
const [todos, setTodos] = React.useState<ITodo[]>([
{
description: 'First Todo',
isChecked: true
}
]);
const { showMessage } = useInjectable<ITodoService>(ITodoService);
const template = ({ data, index }: { data: ITodo; index: number }) => {
const handlerChange = () => {
const newTodos = todos.slice(0);
newTodos.splice(index, 1, {
description: data.description,
isChecked: !data.isChecked
});
showMessage(`Set ${data.description} to be ${!data.isChecked}`);
setTodos(newTodos);
};
return (
<div className={styles.todo_item} key={`${data.description + index}`}>
<CheckBox
checked={data.isChecked}
onChange={handlerChange}
label={data.description}
/>
</div>
);
};
return (
<RecycleList
height={height}
width={width}
itemHeight={24}
data={todos}
template={template}
/>
);
};Effect Show

Add Items Using shortcut keys
Further, we can also register commands and shortcut keys through the contribution point mechanism, with the ability to add Todo items with the help of IQuickInputService.
import { Injectable, Autowired } from '@opensumi/di';
import { IMessageService } from '@opensumi/ide-overlay';
import { Emitter, IQuickInputService } from '@opensumi/ide-core-browser';
import { ITodoService } from '../common';
@Injectable()
export class TodoService implements ITodoService {
@Autowired(IMessageService)
private messageService: IMessageService;
@Autowired(IQuickInputService)
private quickInputService: IQuickInputService;
private onDidChangeEmitter: Emitter<string> = new Emitter();
get onDidChange() {
return this.onDidChangeEmitter.event;
}
showMessage = (message: string) => {
this.messageService.info(message);
};
addTodo = async () => {
const param = await this.quickInputService.open({
placeHolder: 'Enter your plan',
value: ''
});
if (param !== undefined && param !== null) {
this.onDidChangeEmitter.fire(param);
}
};
}Registration of commands and shortcut keys:
import { Autowired } from '@opensumi/di';
import {
CommandContribution,
CommandRegistry,
Domain,
KeybindingContribution,
KeybindingRegistry,
localize
} from '@opensumi/ide-core-browser';
import { EXPLORER_CONTAINER_ID } from '@opensumi/ide-explorer/lib/browser/explorer-contribution';
import {
MainLayoutContribution,
IMainLayoutService
} from '@opensumi/ide-main-layout';
import { ITodoService, TODO_COMMANDS } from '../common';
import { Todo } from './todo.view';
@Domain(MainLayoutContribution, CommandContribution, KeybindingContribution)
export class TodoContribution
implements
MainLayoutContribution,
CommandContribution,
KeybindingContribution {
@Autowired(IMainLayoutService)
private mainLayoutService: IMainLayoutService;
@Autowired(ITodoService)
private todoService: ITodoService;
onDidRender() {
this.mainLayoutService.collectViewComponent(
{
component: Todo,
collapsed: false,
id: 'todo-view',
name: 'Todo'
},
EXPLORER_CONTAINER_ID
);
}
registerCommands(registry: CommandRegistry) {
registry.registerCommand(TODO_COMMANDS.ADD_TODO, {
execute: () => {
return this.todoService.addTodo();
}
});
}
registerKeybindings(registry: KeybindingRegistry) {
registry.registerKeybinding({
keybinding: 'cmd+o',
command: TODO_COMMANDS.ADD_TODO.id
});
}
}Introduce onDidChange to the view so everytime after you adding a Todo item by shortcut keys, the item will be rendered and show up:
// modules/todo/browser/todo.view.tsx
...
export const Todo = ({
viewState
}: React.PropsWithChildren<{ viewState: ViewState }>) => {
...
const { showMessage, onDidChange } = useInjectable<ITodoService>(ITodoService);
React.useEffect(() => {
const disposable = onDidChange((value: string) => {
const newTodos = todos.slice(0);
newTodos.push({
description: value,
isChecked: false,
});
setTodos(newTodos);
});
return () => {
disposable.dispose();
};
}, [todos]);
...
};Results Show
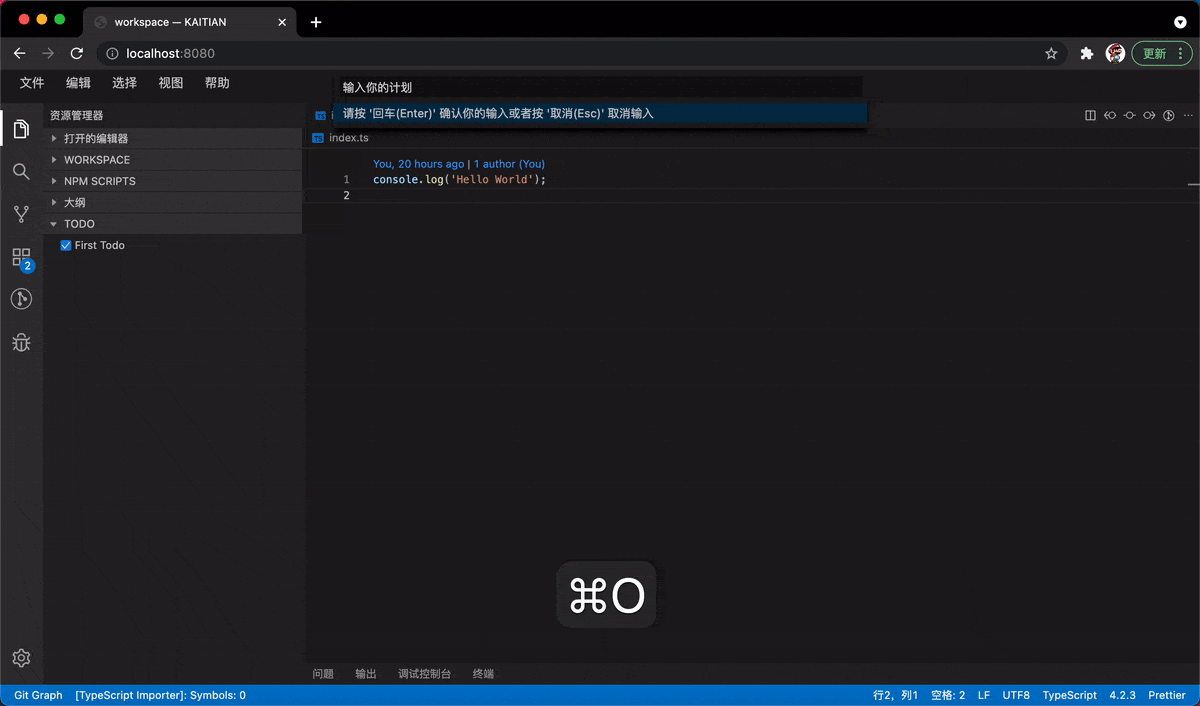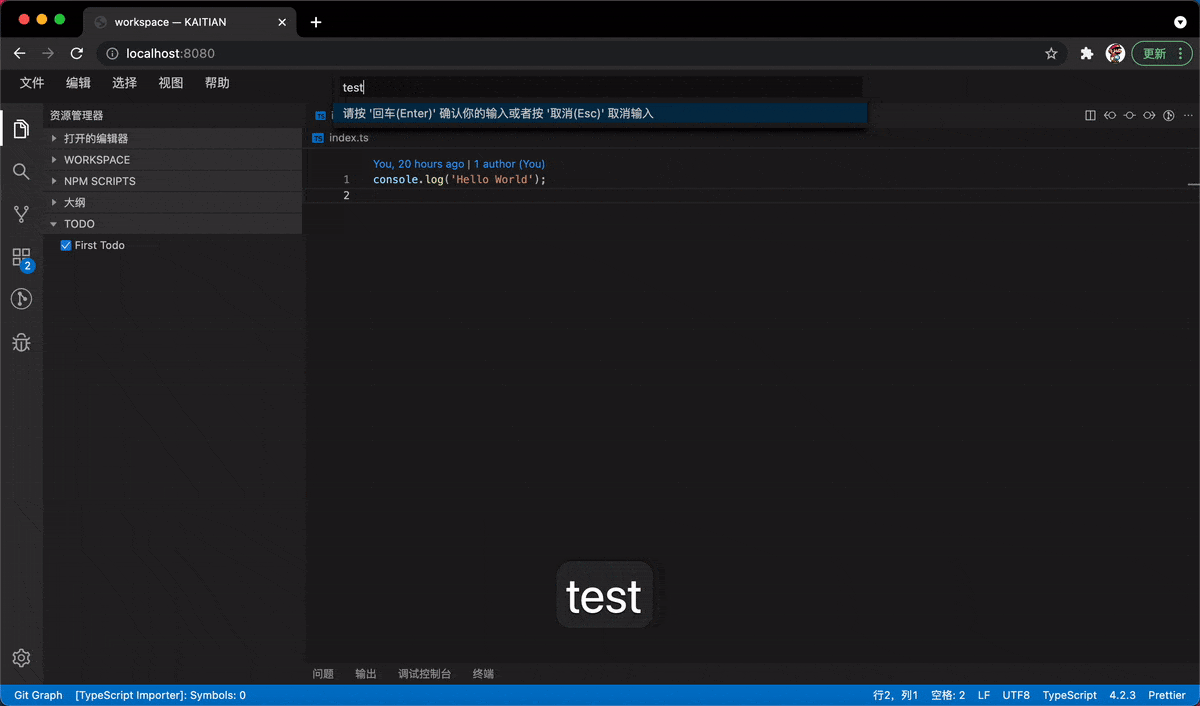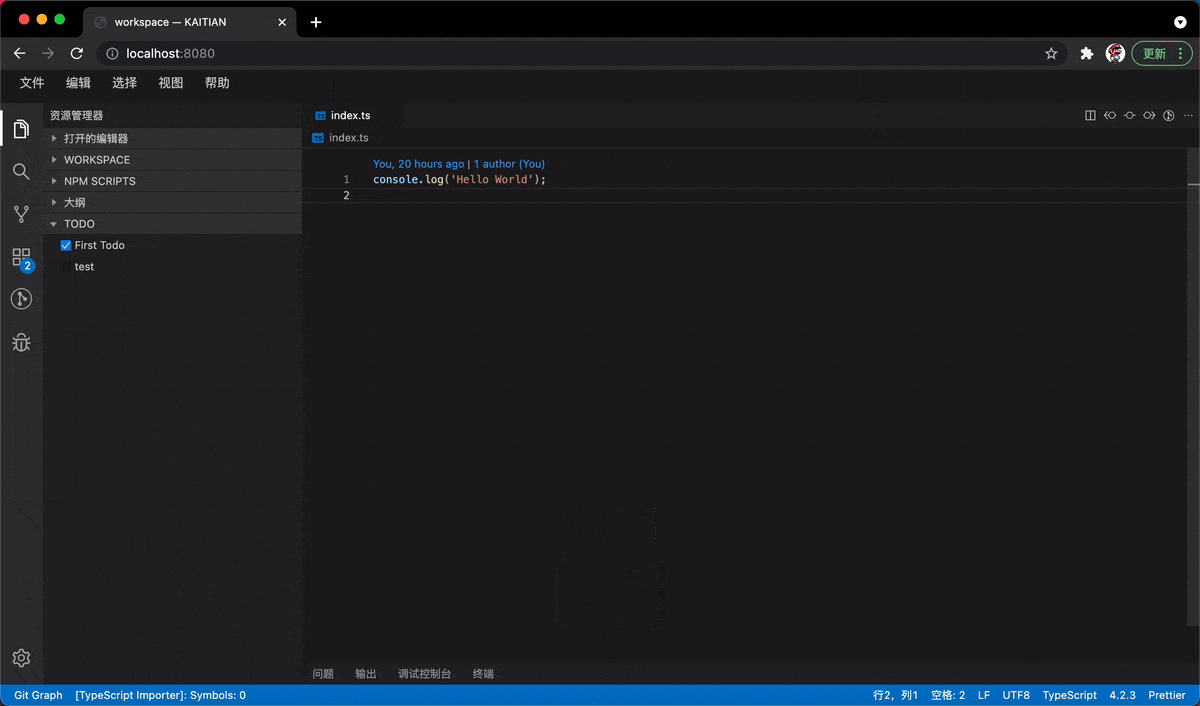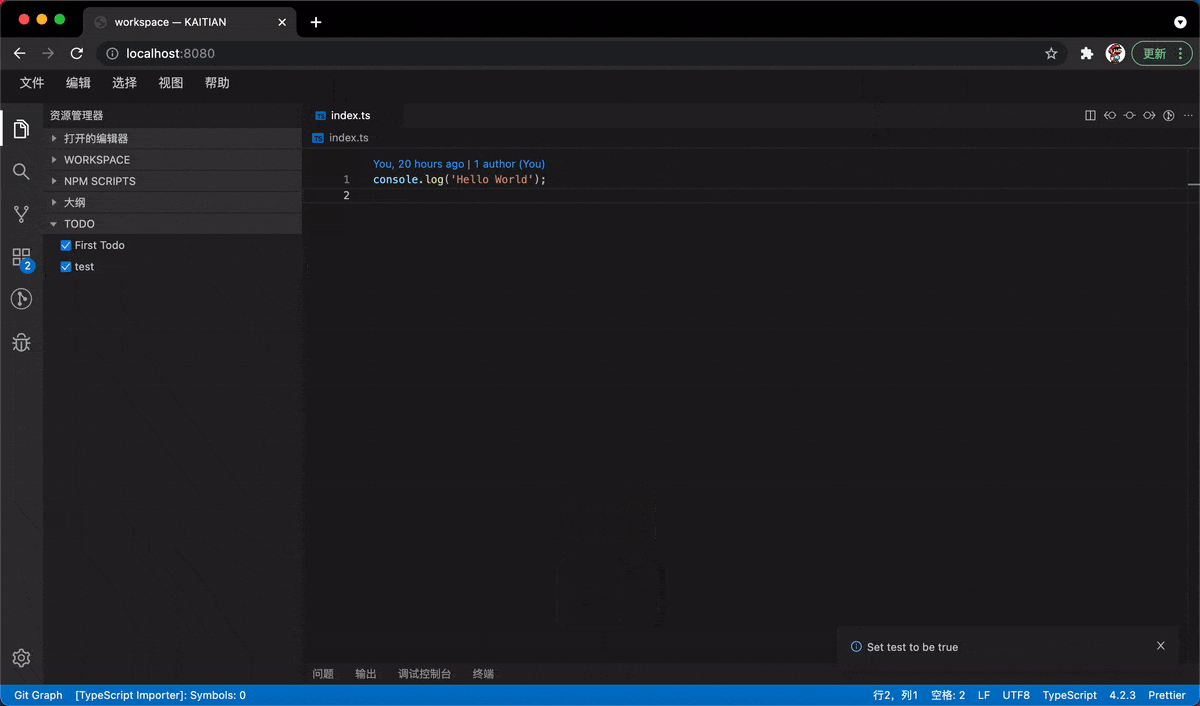
In the next section, we will take a close look at both frontend and backend two-way communication to invoke a two-way service.
